Blog - Channel Partner
How Microsoft Manages Tax Remittance on Azure Marketplace: A Comprehensive Guide

The Azure Marketplace is a powerful platform that enables organizations to buy and sell cloud solutions and services. However, dealing with the tax implications of selling across various countries can be challenging, especially given the differing tax regulations. To simplify this process for sellers, Microsoft manages tax remittances in certain countries, alleviating the burden of understanding and adhering to complex tax requirements. This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of how Microsoft manages tax remittance in specific countries, how it handles these taxes, and what sellers need to know about managing taxes in countries where Microsoft does not handle tax remittance.
It is important that you consult a tax professional within your region to fully understand and manage the tax process connected to Microsoft Azure Marketplace.
---
Countries Where Microsoft Manages Tax Remittance
Microsoft provides tax remittance services in several countries, effectively handling the collection, reporting, and payment of taxes on behalf of sellers who transact on the Azure Marketplace. Here are some of the key countries where Microsoft manages tax remittance, this list is continuously updated and changed, so please verify the latest version:
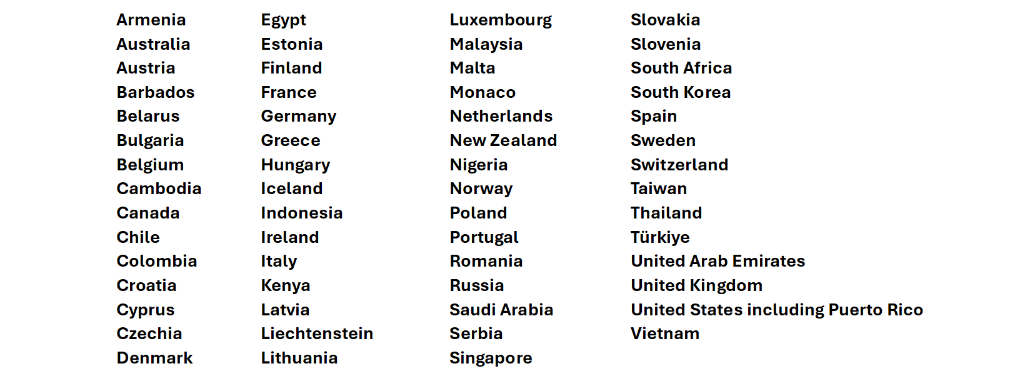
In these countries, Microsoft takes the responsibility of calculating, collecting, and remitting taxes directly to the local tax authorities. This simplifies the process for sellers and ensures compliance with local tax laws.
How Microsoft Handles Tax Remittance
Microsoft's tax handling process involves several steps, ensuring that sellers remain compliant with local tax regulations while focusing on their core business activities. Here is a breakdown of how Microsoft handles tax remittance:
1. Tax Calculation: Microsoft automatically calculates the applicable tax for each transaction based on the buyer's location and the type of product or service sold. This calculation takes into account the specific tax rate for the country, which may include Value-Added Tax (VAT), Goods and Services Tax (GST), or other local sales taxes.
2. Tax Collection: Once the applicable tax is calculated, Microsoft collects the tax amount from the buyer at the point of sale. The collected tax is then added to the transaction amount, ensuring that the buyer is charged the correct amount, inclusive of taxes.
3. Tax Reporting and Remittance: Microsoft is responsible for reporting and remitting the collected taxes to the appropriate tax authorities. This includes filing tax returns and making payments on behalf of the sellers. Sellers do not need to worry about filing their own tax returns or making direct payments to tax authorities in these countries.
4. Tax Invoicing: Microsoft issues tax-compliant invoices to buyers that include the breakdown of the tax amount. This invoice serves as proof of payment and can be used for accounting and tax purposes by both the seller and the buyer.
5. Tax Documentation and Compliance: Microsoft ensures that all necessary tax documentation is maintained and that all transactions are compliant with local tax laws. This includes maintaining records of tax filings, payments, and any communications with tax authorities.
Benefits of Microsoft Managing Tax Remittance
-
Reduced Compliance Burden: Sellers are relieved from the complexity of managing taxes across multiple jurisdictions.
-
Accurate Tax Handling: Microsoft uses advanced tax engines to ensure accurate tax calculation, reducing the risk of errors.
-
Focus on Business: Sellers can focus on their core competencies without worrying about tax compliance.
-
Streamlined Invoicing: Automatic generation of tax-compliant invoices reduces administrative work for sellers.
Countries Where Microsoft Does Not Manage Tax Remittance
While Microsoft manages tax remittance in many countries, there are still several countries where sellers are responsible for handling their own tax obligations when transacting on the Azure Marketplace. Some of these countries include, this list is continuously updated and changed, so please verify the latest version:


In these countries, Microsoft does not handle tax calculation, collection, or remittance. Instead, sellers are required to manage their tax obligations independently.
How to Handle Tax Remittance in Countries Where Microsoft Does Not Manage It
For countries where Microsoft does not manage tax remittance, sellers must take responsibility for complying with local tax laws. Here’s what sellers need to consider when managing tax remittances in these countries:
1. Understand Local Tax Regulations: Sellers must familiarize themselves with the tax regulations in each country where they sell their products or services. This includes
understanding the applicable tax types (such as VAT, GST, or sales tax), tax rates, and filing requirements.
2. Register for Tax Purposes: In many countries, sellers need to register for tax purposes if they exceed certain thresholds for sales. This may involve obtaining a local tax identification number and registering with the relevant tax authorities.
3. Calculate and Collect Taxes: Sellers need to implement systems to calculate and collect the appropriate taxes from buyers. This could involve using tax calculation software or working with third-party tax service providers who specialize in international tax compliance.
4. Issue Tax-Compliant Invoices: Sellers must ensure that they issue tax-compliant invoices that include the breakdown of the tax amount and any necessary tax registration details. This is important for both accounting purposes and for buyers who may need these invoices for their own tax filings.
5. File Tax Returns and Remit Taxes: Sellers are responsible for filing tax returns and remitting the collected taxes to the appropriate tax authorities within the required deadlines. This may involve quarterly or annual filings, depending on the country.
6. Maintain Tax Records: It is essential for sellers to maintain accurate records of all transactions, tax filings, and payments. These records may be required for audits or other tax-related inquiries from local authorities.
7. Consult for Professional Tax Advice: Given the complexities of international tax compliance, it is often beneficial for sellers to consult with tax professionals who have expertise in the specific countries where they operate. This can help ensure that they remain compliant and avoid potential penalties.
Managing tax remittance on the Azure Marketplace can be complex, especially for sellers operating in multiple countries with different tax regulations. Microsoft’s tax remittance services in countries like the United States, Canada, Australia, and the EU help simplify this process by handling tax calculation, collection, and remittance on behalf of sellers. However, in countries where Microsoft does not manage tax remittance, sellers must take on the responsibility of complying with local tax laws, including registering for tax purposes, calculating and collecting taxes, issuing tax-compliant invoices, and filing tax returns.
By understanding the specific tax requirements in each country and leveraging the right tools and professional advice, sellers can navigate the complexities of international tax compliance and focus on growing their businesses on the Azure Marketplace.
For further discussion regarding the Azure Marketplace, please connect with your SureStep Ambassador at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..


